
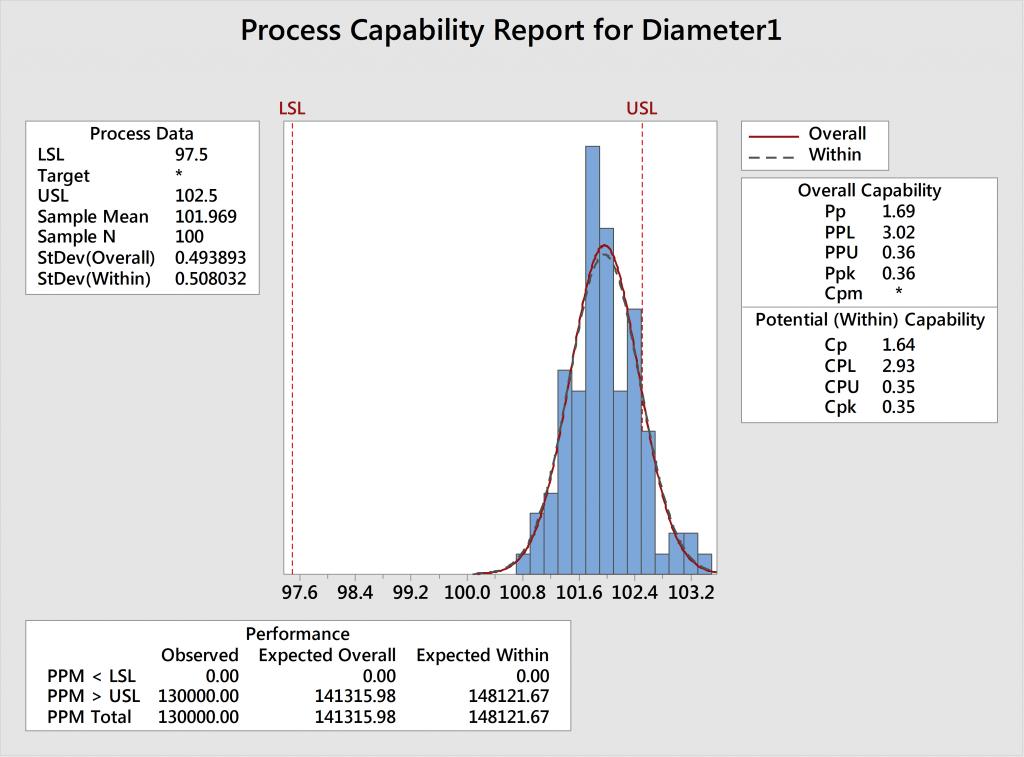
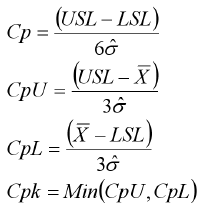
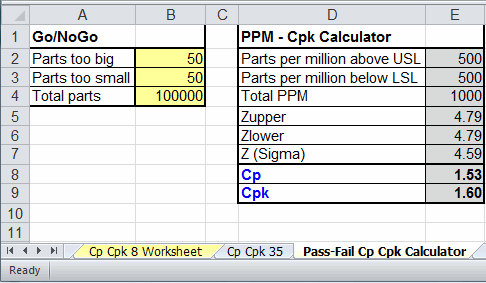
By comparing PPM values before and after a process improvement, you can get a concrete sense of how much a process improvement has actually reduced the number of nonconforming parts on both sides of the process curve. The lower control limit LCL and the upper control limit UCL of a process may be calculated from the mean and. PPM Total indicates the total number of nonconforming parts outside of both specification limits. Statistical Process Control (SPC) ( of 4). PPM USL indicates the number of nonconforming parts greater than the upper specification limit. To get a clearer indication of how the process is performing on both sides of the process curve, you can use other indices, such as PPM. One of the primary goals of statistical process control is to reduce the probability of a defect, however you define it, to acceptable levels. Therefore they evaluate only one side of the process curve, and do not directly indicate how the process performs on the other side of the process curve. By convention established at Motorola, where the Six Sigma program originated, the Sigma level is adjusted by 1.5 sigma to recognize the tendency of processes to.
Also shown is a direct conversion to a Cpk level based on the area under a Normal Curve. Using the table above, the sigma level is found to be 4 sigmas. Although Cpk and Ppk are the most commonly used metrics for process capability, they measure how the process is performing only in relation to the specification limit that is closest to the process mean. The following table lists Defects Per Million Opportunities with the corresponding Sigma Level. Using the formula DPMO Total defects / (sample sizeopportunities for failure per item) 1,000,000.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
